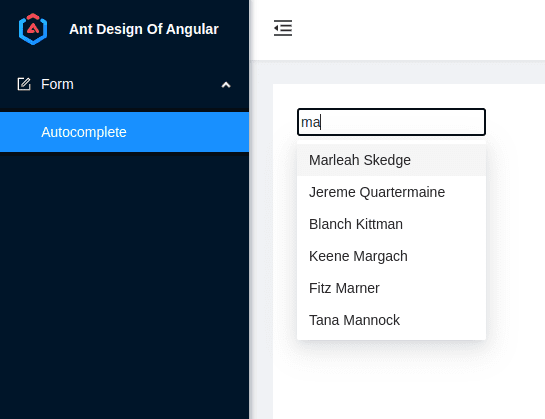
1. Introduction
The NgZorro is an Angular library with many valuable components that could be used in web applications. In this tutorial, we will present the NgZorro Autocomplete component powered by data from the Spring Boot application server.
2. Spring Boot Project
The backend site was powered by the Spring framework with several features such as liquibase, Spring Data, Specifications, or Rest Controllers.
2.1. Project Structure
The file structure of the backend project is as follows:
├── main
│ ├── java
│ │ └── com
│ │ └── frontbackend
│ │ └── springboot
│ │ ├── config
│ │ │ └── CorsFilter.java
│ │ ├── dto
│ │ │ └── PersonDto.java
│ │ ├── jpa
│ │ │ ├── model
│ │ │ │ └── PersonEntity.java
│ │ │ ├── repository
│ │ │ │ └── PersonRepository.java
│ │ │ └── utils
│ │ │ └── JpaSpecifications.java
│ │ ├── rest
│ │ │ └── PersonController.java
│ │ ├── service
│ │ │ └── PersonService.java
│ │ └── SpringBootAngularNgZorroAutocomplete.java
│ └── resources
│ ├── application.properties
│ └── db-scripts
│ ├── db-changelog-master.xml
│ └── PERSON-1.0.0.xml
The individual components used on the backend are described below.
2.2. Maven
Maven pom.xml file used to build the project has the following content:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<artifactId>spring-boot-postgresql-angular-ng-zorro-autocomplete</artifactId>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.5.0</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<properties>
<lombok.version>1.18.24</lombok.version>
<liquibase-core.version>4.16.0</liquibase-core.version>
</properties>
<!-- Add typical dependencies for a web application -->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.postgresql</groupId>
<artifactId>postgresql</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>${lombok.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.liquibase</groupId>
<artifactId>liquibase-core</artifactId>
<version>${liquibase-core.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<!-- Package as an executable jar -->
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
We used several dependencies:
- org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web:2.5.0 - Spring Boot web application,
- org.projectlombok:lombok:1.18.24 - library for generating common methods, like setters and getters, for POJO objects,
- org.postgresql:postgresql - drivers for PostgreSQL database.
- org.liquibase:liquibase-core:4.16.0 - liquibase-core.
Notice, that in order to create an executable jar we added a special spring-boot-maven-plugin plugin:
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
2.3. REST API
The application will serve the following services:
| URL | HTTP Method | Action |
| /api/people?filter={filter} | GET | Get filtered list of people |
2.4. Model, Controller, and Service
The PersonEntity class is a Java representation of tbl_person table in the PostgreSQL database:
package com.frontbackend.springboot.jpa.model;
import java.util.UUID;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Setter;
import org.hibernate.annotations.Type;
@Entity(name = "tbl_person")
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Setter
@Getter
public class PersonEntity {
@Id
@Type(type = "pg-uuid")
private UUID id;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private int age;
private String address;
}
The PersonRepository is our JpaRepository used for CRUD operations on the PersonEntity object. Note that this interface also extends JpaSpecificationExecutor to create queries using Specifications.
package com.frontbackend.springboot.jpa.repository;
import com.frontbackend.springboot.jpa.model.PersonEntity;
import java.util.UUID;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaSpecificationExecutor;
public interface PersonRepository extends JpaRepository<PersonEntity, UUID>, JpaSpecificationExecutor<PersonEntity> {
}
The JpaSpecifications is the utility class used for preparing database queries:
package com.frontbackend.springboot.jpa.utils;
import java.util.List;
import lombok.experimental.UtilityClass;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.domain.Specification;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
@UtilityClass
public class JpaSpecifications {
public <T> Specification<T> upperLike(String value, String columnName) {
return !StringUtils.hasText(value) ?
null :
((root, query, cb) -> cb.like(cb.upper(root.get(columnName)), "%" + value.toUpperCase() + "%"));
}
public <T> Specification<T> checkList(List<?> values, String columnName) {
return (values == null || values.isEmpty()) ?
null :
((root, query, cb) -> root.get(columnName)
.in(values));
}
}
PersonService is responsible for preparing queries and mapping database results into DTO objects:
package com.frontbackend.springboot.service;
import static org.springframework.data.jpa.domain.Specification.where;
import com.frontbackend.springboot.dto.PersonDto;
import com.frontbackend.springboot.jpa.model.PersonEntity;
import com.frontbackend.springboot.jpa.repository.PersonRepository;
import com.frontbackend.springboot.jpa.utils.JpaSpecifications;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.data.domain.PageRequest;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.domain.Specification;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Service
public class PersonService {
private static final int PAGE_SIZE = 10;
private static final int PAGE_NUMBER = 0;
private final PersonRepository personRepository;
public List<PersonDto> findPerson(@RequestParam String filter) {
return personRepository.findAll(applyWhere(filter), PageRequest.of(PAGE_NUMBER, PAGE_SIZE))
.stream()
.map(this::toPersonDto)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
private Specification<PersonEntity> applyWhere(String filter) {
Specification<PersonEntity> firstName = JpaSpecifications.upperLike(filter, "firstName");
Specification<PersonEntity> lastName = JpaSpecifications.upperLike(filter, "lastName");
return where(firstName).or(lastName);
}
private PersonDto toPersonDto(PersonEntity entity) {
return PersonDto.builder()
.id(entity.getId())
.name(entity.getFirstName() + " " + entity.getLastName())
.age(entity.getAge())
.address(entity.getAddress())
.build();
}
}
The PersonController is our REST controller used to handle communication with the frontend site:
package com.frontbackend.springboot.rest;
import com.frontbackend.springboot.dto.PersonDto;
import com.frontbackend.springboot.service.PersonService;
import java.util.List;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/people")
public class PersonController {
private final PersonService personService;
@GetMapping
public List<PersonDto> findPerson(@RequestParam("filter") String filter) {
return personService.findPerson(filter);
}
}
The PersonDto is our Data Transfer Object used by REST controller:
package com.frontbackend.springboot.dto;
import java.util.UUID;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Getter;
@Builder
@Getter
public class PersonDto {
private UUID id;
private String name;
private int age;
private String address;
}
2.5. Spring Boot Configuration
The Spring Boot configuration file contains Datasource and liquibase properties:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/db
spring.datasource.username=username
spring.datasource.password=password
spring.liquibase.change-log=classpath:/db-scripts/db-changelog-master.xml
The /db-scripts/db-changelog-master.xml file has the following content:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="no"?>
<databaseChangeLog xmlns="http://www.liquibase.org/xml/ns/dbchangelog"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.liquibase.org/xml/ns/dbchangelog http://www.liquibase.org/xml/ns/dbchangelog/dbchangelog-3.4.xsd">
<include file="db-scripts/PERSON-1.0.0.xml"/>
</databaseChangeLog>
The PERSON-1.0.0.xml stores information about the structure of the tbl_person table and inserts used to fill that table on startup:
?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="no"?>
<databaseChangeLog xmlns="http://www.liquibase.org/xml/ns/dbchangelog"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.liquibase.org/xml/ns/dbchangelog http://www.liquibase.org/xml/ns/dbchangelog/dbchangelog-3.4.xsd">
<changeSet author="frontbackend" id="1.0.0-1">
<createTable tableName="tbl_person">
<column name="id" type="uuid">
<constraints nullable="false"
primaryKey="true"
unique="true"/>
</column>
<column name="first_name" type="VARCHAR2(30)"/>
<column name="last_name" type="VARCHAR2(30)"/>
<column name="age" type="VARCHAR2(500)"/>
<column name="address" type="VARCHAR2(200)"/>
</createTable>
</changeSet>
<changeSet author="frontbackend" id="1.0.0-2">
<sql>
insert into tbl_person (id, first_name, last_name, age, address) values ('597f4585-aa32-4606-bcc5-ae070616de3b', 'Worden', 'Handes', 29, '4566 Di Loreto Park');
insert into tbl_person (id, first_name, last_name, age, address) values ('fb3013fb-5343-4832-ac95-1ee6f0fa264d', 'Eddie', 'Kivits', 48, '97525 Oakridge Trail');
...
</sql>
</changeSet>
</databaseChangeLog>
3. Angular Project
The frontend site is an Angular application that communicates with the backend using REST API.
3.1. Project Structure
The file structure of the frontend project is as follows:
├── app.component.html
├── app.component.scss
├── app.component.spec.ts
├── app.component.ts
├── app.module.ts
├── app-routing.module.ts
├── icons-provider.module.ts
├── model
│ └── person.ts
├── pages
│ ├── autocomplete
│ │ ├── autocomplete.component.html
│ │ ├── autocomplete.component.scss
│ │ ├── autocomplete.component.ts
│ │ ├── autocomplete.module.ts
│ │ └── autocomplete-routing.module.ts
│ └── welcome
│ ├── welcome.component.html
│ ├── welcome.component.scss
│ ├── welcome.component.ts
│ ├── welcome.module.ts
│ └── welcome-routing.module.ts
└── services
└── person-http.service.ts
3.2. Creating Angular Project and Components
To create an Angular project with components and services we used Angular-CLI tool:
3.2.1. Create Angular Project
The following command creates a new Angular project called autocomplete:
ng new autocomplete
The output:
? Would you like to add Angular routing? Yes
? Which stylesheet format would you like to use? SCSS [ https://sass-lang.com/documentation/syntax#scss ]
CREATE autocomplete/README.md (1058 bytes)
CREATE autocomplete/.editorconfig (274 bytes)
CREATE autocomplete/.gitignore (548 bytes)
CREATE autocomplete/angular.json (3243 bytes)
CREATE autocomplete/package.json (1075 bytes)
CREATE autocomplete/tsconfig.json (863 bytes)
CREATE autocomplete/.browserslistrc (600 bytes)
CREATE autocomplete/karma.conf.js (1429 bytes)
CREATE autocomplete/tsconfig.app.json (287 bytes)
CREATE autocomplete/tsconfig.spec.json (333 bytes)
CREATE autocomplete/.vscode/extensions.json (130 bytes)
CREATE autocomplete/.vscode/launch.json (474 bytes)
CREATE autocomplete/.vscode/tasks.json (938 bytes)
CREATE autocomplete/src/favicon.ico (948 bytes)
CREATE autocomplete/src/index.html (298 bytes)
CREATE autocomplete/src/main.ts (372 bytes)
CREATE autocomplete/src/polyfills.ts (2338 bytes)
CREATE autocomplete/src/styles.scss (80 bytes)
CREATE autocomplete/src/test.ts (745 bytes)
CREATE autocomplete/src/assets/.gitkeep (0 bytes)
CREATE autocomplete/src/environments/environment.prod.ts (51 bytes)
CREATE autocomplete/src/environments/environment.ts (658 bytes)
CREATE autocomplete/src/app/app-routing.module.ts (245 bytes)
CREATE autocomplete/src/app/app.module.ts (393 bytes)
CREATE autocomplete/src/app/app.component.scss (0 bytes)
CREATE autocomplete/src/app/app.component.html (23364 bytes)
CREATE autocomplete/src/app/app.component.spec.ts (1091 bytes)
CREATE autocomplete/src/app/app.component.ts (217 bytes)
✔ Packages installed successfully.
Directory is already under version control. Skipping initialization of git.
3.2.2. Add ng-zorro-antd library
To add the ng-zorro-antd library we need to run the following command:
ng add ng-zorro-antd
The output:
ℹ Using package manager: npm
✔ Found compatible package version: ng-zorro-antd@13.4.0.
✔ Package information loaded.
The package ng-zorro-antd@13.4.0 will be installed and executed.
Would you like to proceed? Yes
✔ Package successfully installed.
? Enable icon dynamic loading [ Detail: https://ng.ant.design/components/icon/en ] Yes
? Set up custom theme file [ Detail: https://ng.ant.design/docs/customize-theme/en ] No
? Choose your locale code: en_US
? Choose template to create project: sidemenu
CREATE src/app/icons-provider.module.ts (482 bytes)
CREATE src/app/pages/welcome/welcome-routing.module.ts (352 bytes)
CREATE src/app/pages/welcome/welcome.component.scss (0 bytes)
CREATE src/app/pages/welcome/welcome.component.html (0 bytes)
CREATE src/app/pages/welcome/welcome.component.ts (274 bytes)
CREATE src/app/pages/welcome/welcome.module.ts (314 bytes)
UPDATE package.json (1106 bytes)
UPDATE src/app/app.module.ts (1127 bytes)
UPDATE angular.json (3566 bytes)
UPDATE src/app/app-routing.module.ts (416 bytes)
UPDATE src/app/app.component.scss (1245 bytes)
UPDATE src/app/app.component.html (1592 bytes)
UPDATE src/app/app.component.ts (214 bytes)
✔ Packages installed successfully.
3.2.3. Add modules, components, and services
Next single-line command creates the autocomplete module, routing module, and component:
ng g m pages/autocomplete --routing=true && ng g c pages/autocomplete --skip-tests=true -m=pages/autocomplete
The output:
CREATE src/app/pages/autocomplete/autocomplete-routing.module.ts (255 bytes)
CREATE src/app/pages/autocomplete/autocomplete.module.ts (304 bytes)
CREATE src/app/pages/autocomplete/autocomplete.component.scss (0 bytes)
CREATE src/app/pages/autocomplete/autocomplete.component.html (27 bytes)
CREATE src/app/pages/autocomplete/autocomplete.component.ts (300 bytes)
UPDATE src/app/pages/autocomplete/autocomplete.module.ts (399 bytes)
3.3. Model, Components, and Services
The Person interface is a TypeScript representation of the PersonDto object:
export interface Person {
id: string;
name: string;
age: number;
address: string;
}
The PersonHttpService class is responsible for communication with /api/people endpoint:
import { HttpClient, HttpParams } from '@angular/common/http';
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { Observable } from 'rxjs';
import { Person } from '../model/person';
import { environment } from '../../environments/environment';
const BASE_URL = environment.baseUrl;
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class PersonHttpService {
constructor(private http: HttpClient) {
}
filter(name: string): Observable<Person[]> {
let params = new HttpParams().set('filter', name);
return this.http.get<Person[]>(`${BASE_URL}/api/people`, {params: params});
}
}
The AutocompleteComponent class handle our NgZorro Autocomplete component:
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { PersonHttpService } from '../../services/person-http.service';
@Component({
selector: 'app-autocomplete',
templateUrl: './autocomplete.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./autocomplete.component.scss']
})
export class AutocompleteComponent implements OnInit {
inputValue: string = '';
filteredOptions: string[] = [];
constructor(private personHttpService: PersonHttpService) {
}
ngOnInit(): void {
}
onChange(value: string): void {
this.personHttpService.filter(value).subscribe(list => {
this.filteredOptions = list.map(people => people.name);
});
}
}
The HTML use by AutocompleteComponent:
<div class="example-input">
<input
placeholder='Search people...'
nz-input
[(ngModel)]="inputValue"
(ngModelChange)="onChange($event)"
[nzAutocomplete]="auto"
/>
<nz-autocomplete [nzDataSource]="filteredOptions" #auto></nz-autocomplete>
</div>
In AutocompleteModule we imported the necessary modules from Angular and NgZorro library:
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { CommonModule } from '@angular/common';
import { AutocompleteRoutingModule } from './autocomplete-routing.module';
import { AutocompleteComponent } from './autocomplete.component';
import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
import { NzAutocompleteModule } from 'ng-zorro-antd/auto-complete';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AutocompleteComponent
],
imports: [
FormsModule,
CommonModule,
AutocompleteRoutingModule,
NzAutocompleteModule
]
})
export class AutocompleteModule { }
The AutocompleteRoutingModule contains simple routing to AutocompleteComponent:
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { RouterModule, Routes } from '@angular/router';
import { AutocompleteComponent } from './autocomplete.component';
const routes: Routes = [
{path: '', component: AutocompleteComponent},
];
@NgModule({
imports: [RouterModule.forChild(routes)],
exports: [RouterModule]
})
export class AutocompleteRoutingModule {
}
In the main AppRoutingModule we used lazy loading of child components:
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { Routes, RouterModule } from '@angular/router';
const routes: Routes = [
{ path: '', pathMatch: 'full', redirectTo: '/welcome' },
{ path: 'welcome', loadChildren: () => import('./pages/welcome/welcome.module').then(m => m.WelcomeModule) },
{ path: 'autocomplete', loadChildren: () => import('./pages/autocomplete/autocomplete.module').then(m => m.AutocompleteModule) }
];
@NgModule({
imports: [RouterModule.forRoot(routes)],
exports: [RouterModule]
})
export class AppRoutingModule { }
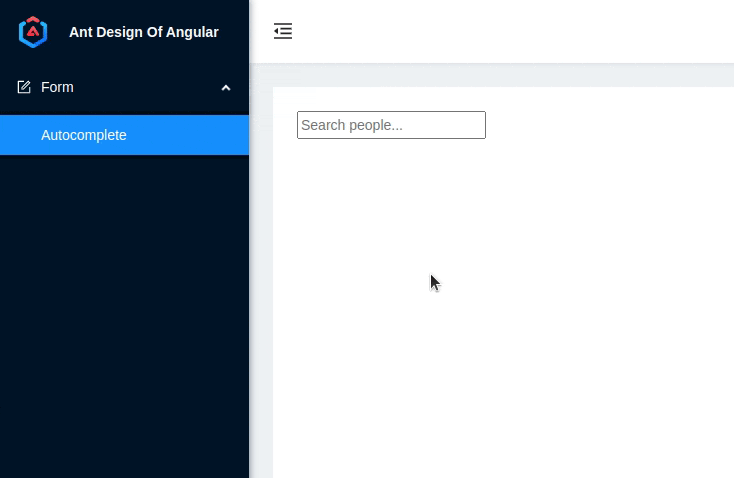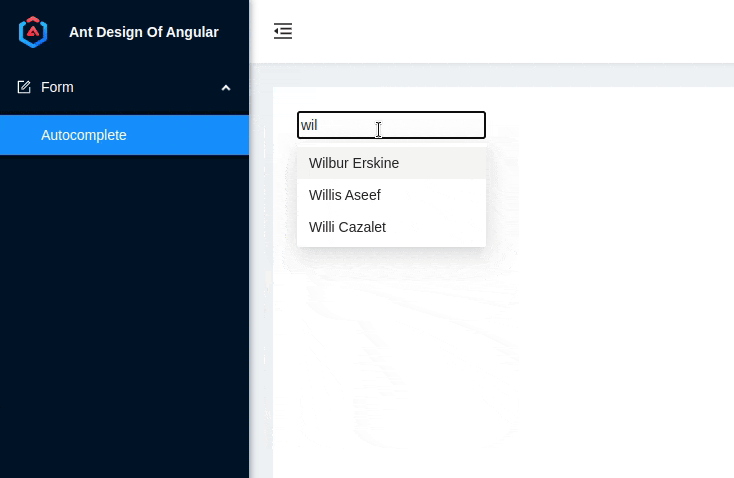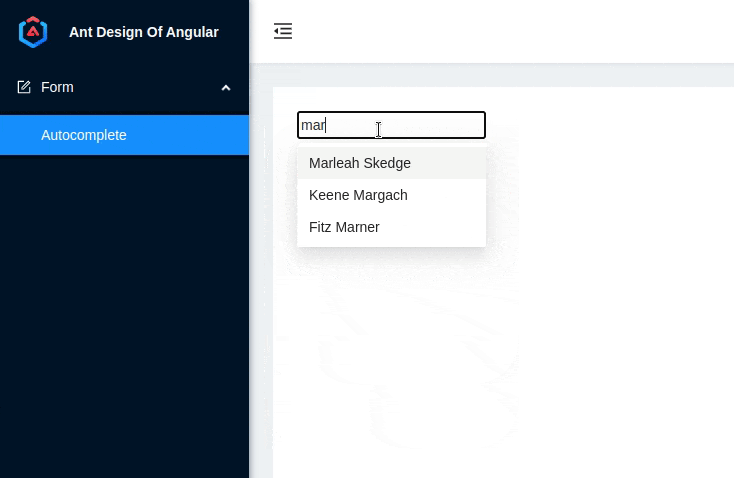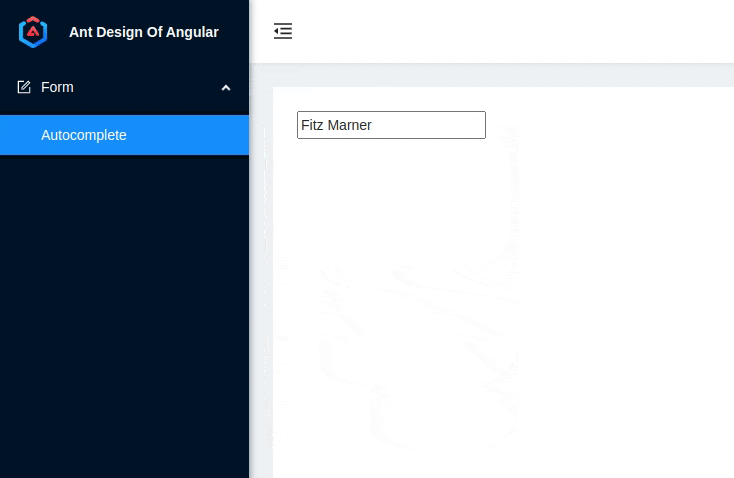
4. Demo
5. Conclusion
In this tutorial, we presented how to handle the NgZorro Autocomplete component powered by data from the Spring Boot application.
{{ 'Comments (%count%)' | trans {count:count} }}
{{ 'Comments are closed.' | trans }}